- Discover the magic of soil amendments and how they can transform your garden.
- Learn about different types of organic and inorganic soil amendments.
- Understand the benefits and drawbacks of each amendment.
- Master the art of choosing the right soil amendment for your specific needs.
Soil amendments are the unsung heroes of the gardening world. These magical ingredients, when mixed into your soil, can dramatically improve its physical properties, creating a thriving environment for your plants. Whether you’re battling clay soil that resembles concrete or sandy soil that drains faster than a sieve, soil amendments are the key to unlocking your garden’s full potential. This guide delves into the world of soil amendments, providing you with the knowledge to choose the perfect blend for your garden.
Contents
- Understanding Soil Amendments
- Exploring Organic vs. Inorganic Amendments
- Organic Amendments: Nature’s Boosters
- Inorganic Amendments: Targeted Solutions
- Delving into Specific Organic Amendments
- Wood Products: A Slow Burn
- Sphagnum and Peat Moss: Water Retention Wonders
- Biosolids: Recycled Resources
- Manure: Nutrient-Rich but Handle with Care
- Worm Castings: Black Gold for Your Garden
- Compost: The Gold Standard
- Choosing the Right Soil Amendment
- Conclusion: Cultivating Success with Soil Amendments
Understanding Soil Amendments
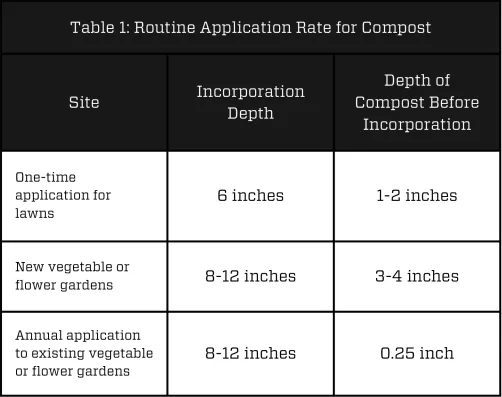
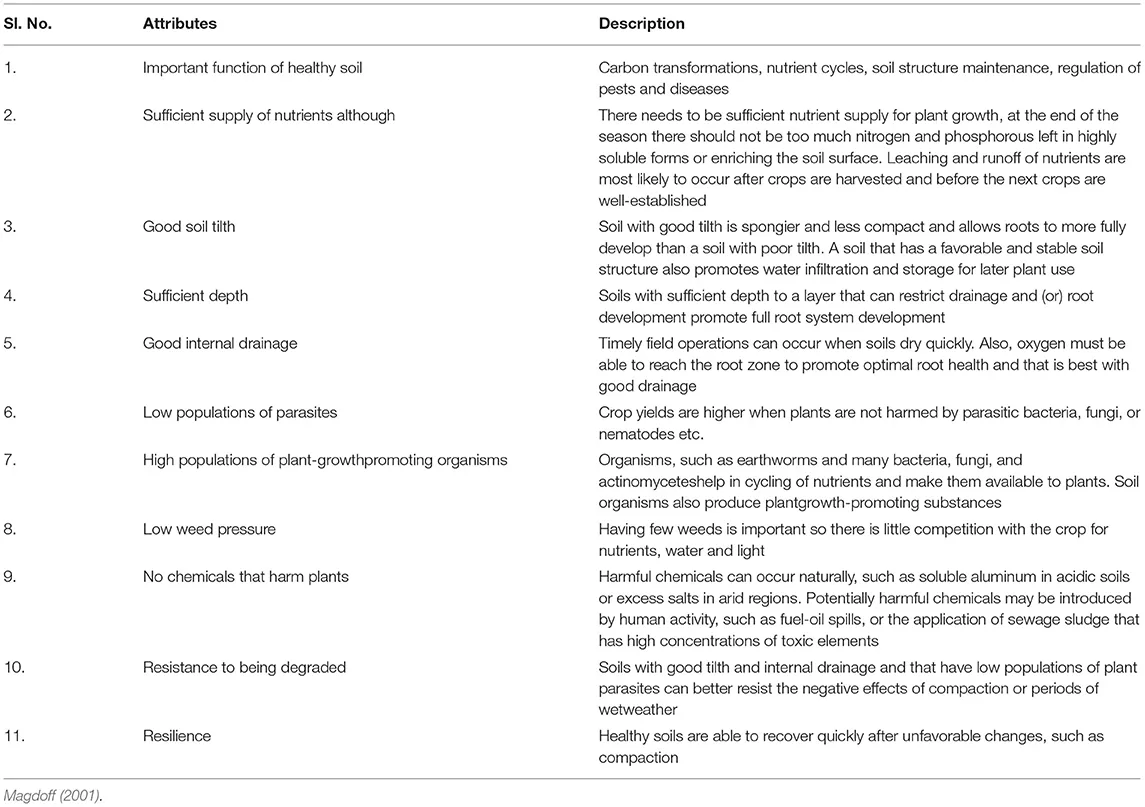
Soil amendments enhance various aspects of soil health, including water retention, permeability, infiltration, drainage, aeration, and structure. The ultimate goal? To create a haven for your plant’s roots. Remember, for an amendment to work its magic, it needs to be thoroughly mixed into the soil, not just sprinkled on top.
Exploring Organic vs. Inorganic Amendments
Soil amendments fall into two main categories: organic and inorganic.
Organic Amendments: Nature’s Boosters
Organic amendments, derived from living materials, are a powerhouse of benefits. They enrich the soil with organic matter, improving aeration, water infiltration, and nutrient retention. Compost, the king of organic amendments, is a readily available option. Other organic choices include aged manure, worm castings, and cover crops.
Inorganic Amendments: Targeted Solutions
Inorganic amendments, derived from minerals or manufactured materials, offer specialized solutions. They are particularly useful for rock gardens, cactus gardens, or areas with heavy foot traffic. Examples include perlite, vermiculite, and sand. However, be cautious when adding inorganic materials like gravel or rock to improve drainage, as studies have shown mixed results, and it can sometimes worsen the problem.
Delving into Specific Organic Amendments
Let’s take a closer look at some popular organic soil amendments:
Wood Products: A Slow Burn
Fresh wood products like sawdust and wood chips are generally avoided as soil amendments. They can temporarily deplete nitrogen in the soil as microorganisms break them down. Composting wood products before use mitigates this issue.
Sphagnum and Peat Moss: Water Retention Wonders
Sphagnum and peat moss are excellent for water retention, especially in sandy soils. However, their harvesting raises environmental concerns due to the slow regeneration of peat bogs. Coconut coir offers a sustainable alternative.
Biosolids: Recycled Resources
Biosolids, byproducts of sewage treatment, can be used as soil amendments, but only EPA Exceptional Quality (EQ) class A biosolids are approved for landscaping and gardens due to concerns about heavy metals and pathogens. They can also be high in salt content.
Manure: Nutrient-Rich but Handle with Care
Fresh manure should never be used as a soil amendment due to the risk of pathogens. Aged or composted manure is a better option, providing valuable nutrients. Be mindful of potential salt content, especially with aged manure.
Worm Castings: Black Gold for Your Garden
Worm castings are a gentle, nutrient-rich amendment. They release nutrients slowly, enriching the soil over time. Avoid direct contact with plants due to potential high salt content.
Compost: The Gold Standard
Compost is the ultimate organic soil amendment. It’s a rich source of nutrients and improves soil structure significantly. Look for compost with 40-60% organic matter. Be aware that compost is not regulated for nutrient content and can vary in quality. Salt content can also be an issue, particularly with manure-based composts.
Choosing the Right Soil Amendment
Selecting the right soil amendment depends on several factors:
- Desired Results: What do you want to achieve? Improved drainage? Better water retention?
- Routine Applications: Will you be amending regularly, such as in a vegetable garden?
- Longevity: Do you need a quick boost or a long-lasting effect?
- Salt Content: Be mindful of potential salt buildup, especially in dry climates.
- Regulations: Check local regulations regarding the use of certain amendments like biosolids.
Conclusion: Cultivating Success with Soil Amendments
Soil amendments are invaluable tools for any gardener. By understanding the different types available and their specific benefits, you can tailor your approach to achieve optimal soil health and vibrant plant growth. Share your experiences with soil amendments in the comments below, and let us know what works best in your garden! Explore more gardening tips and advice on Thelittle.garden.